Choking is a critical emergency that can occur to anyone, especially children. According to the NHS and the British Red Cross, knowing how to react quickly can save a life. This article provides an evidence-based approach to first aid for choking, ensuring you are prepared to help in an emergency.
As both a nurse and a parent, I have witnessed the frightening reality of choking. In both situations, the fear is palpable, and the instinct to react promptly takes over. Whether in a clinical setting or at home, the urgency to provide help becomes second nature. It’s a stark reminder of how important it is to be prepared and knowledgeable about choking first aid.
Understanding Choking: Signs and Symptoms
Choking occurs when an object blocks the airway, preventing normal breathing. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Clutching at the throat or chest
- Inability to speak, breathe, or cough
- High-pitched wheezing or breath sounds
- Turning blue or pale
- Loss of consciousness in severe cases
Recognising these symptoms early can be crucial in responding effectively.
Choking in Adults: First Aid Steps
Mild Choking
If the person can cough, speak, or breathe, encourage them to keep coughing. This may help dislodge the object on its own.
Severe Choking
If the person cannot breathe, speak, or cough, follow these steps:
Step 1: Encourage Coughing
- Ask them to keep coughing if possible, as this may help clear the blockage.
Step 2: Administer Back Blows
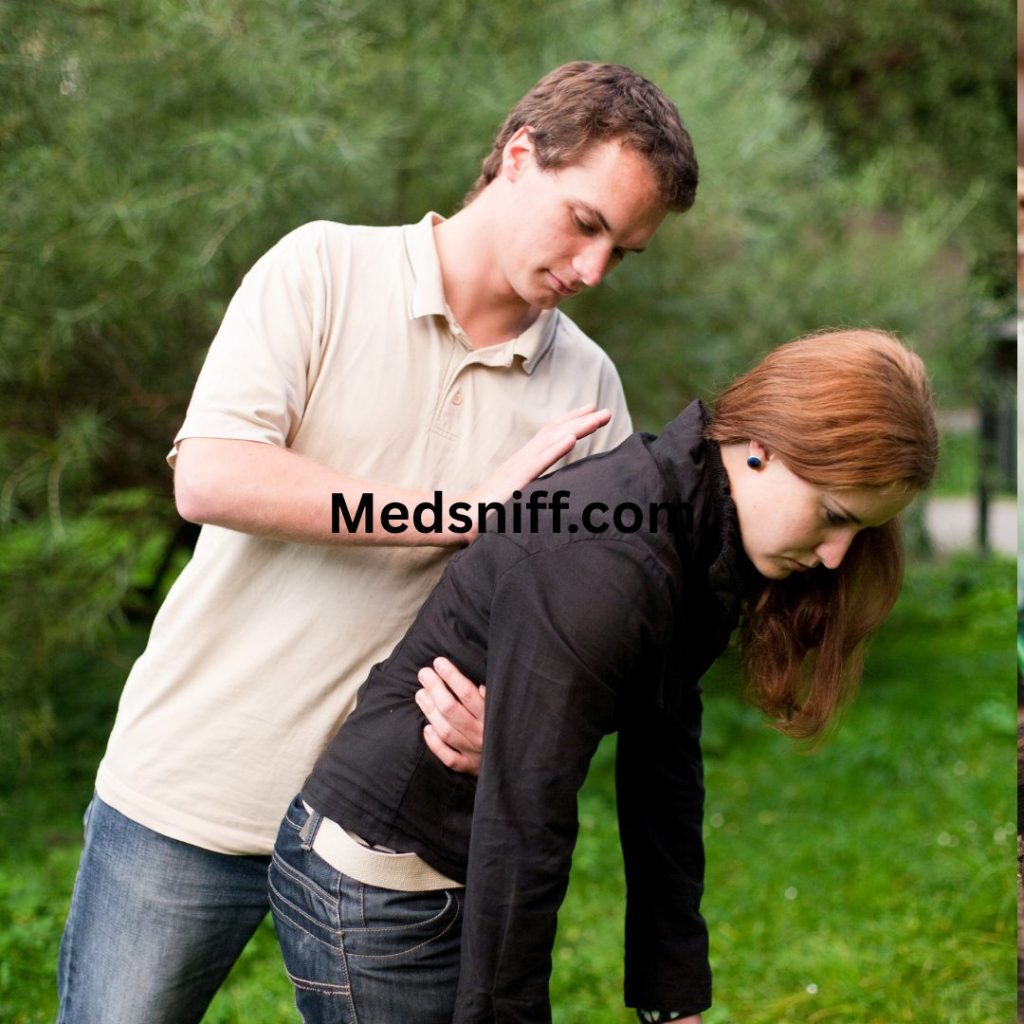

- Stand behind the person and lean them forward slightly.
- Give up to 5 sharp blows between their shoulder blades using the heel of your hand. This creates pressure that may help dislodge the object.
Step 3: Perform Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Manoeuvre)
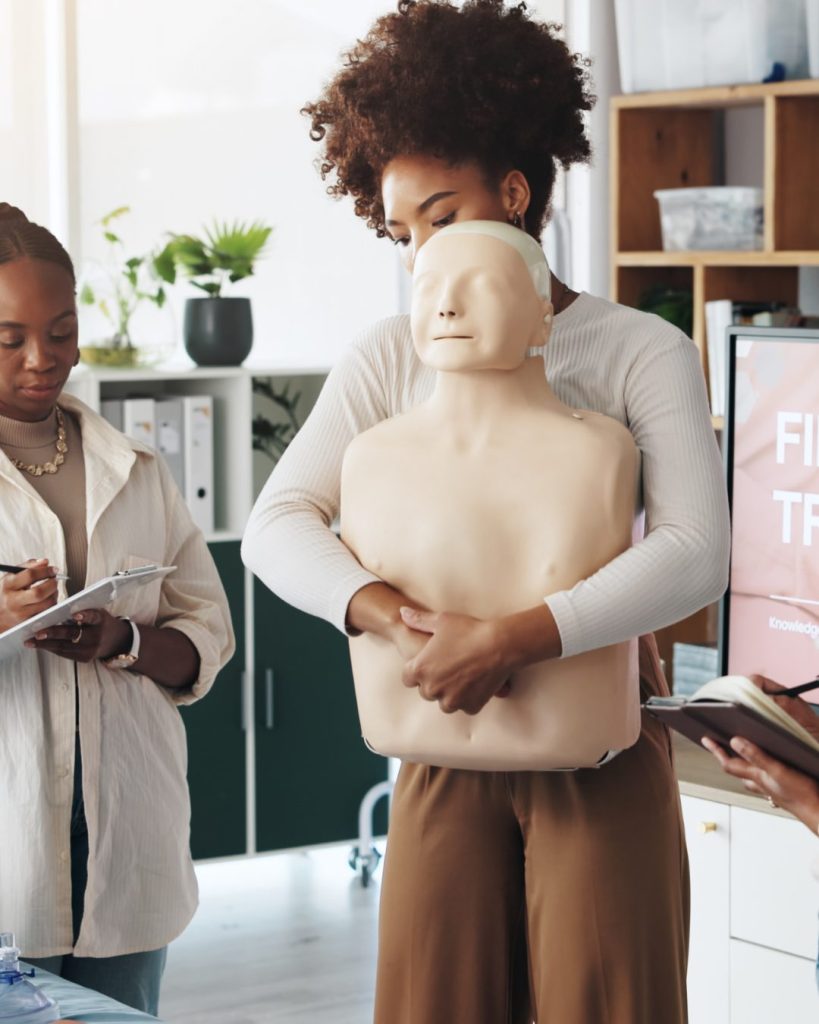

- If back blows do not work, perform abdominal thrusts:
- Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist and position it just above the navel.
- Grasp your fist with the other hand and pull sharply inwards and upwards. Repeat up to 5 times.
Step 4: Call for Help
- If the airway remains blocked, call 999 for emergency assistance. Continue alternating between back blows and abdominal thrusts until help arrives.
Choking in Children: First Aid Steps
Children, especially those aged 1 to 5, are at a high risk of choking due to their tendency to put objects in their mouths.
Signs to Watch For
- Loud coughing
- Difficulty breathing
- Unusual behaviour (e.g., holding their throat)
First Aid Steps for Choking Children

Step 1: Encourage Coughing
- If the child is coughing loudly, encourage them to keep coughing.
Step 2: Administer Back Blows
- Lay the child face down across your lap, or support them in a forward-leaning position.
- Deliver 5 sharp back blows between the shoulder blades with the heel of your hand.
Step 3: Perform Abdominal Thrusts
- If back blows do not work, perform abdominal thrusts:
- Stand behind the child and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist and position it just above the navel.
- Pull sharply inwards and upwards, repeating up to 5 times.
Step 4: Call for Help
- If the object does not dislodge, call 999 for emergency assistance and continue the cycle of back blows and abdominal thrusts.
Choking in Babies: First Aid Steps
Babies are particularly vulnerable to choking. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, parents must know how to respond effectively.
First Aid Steps for Choking Babies (Under 1 Year)
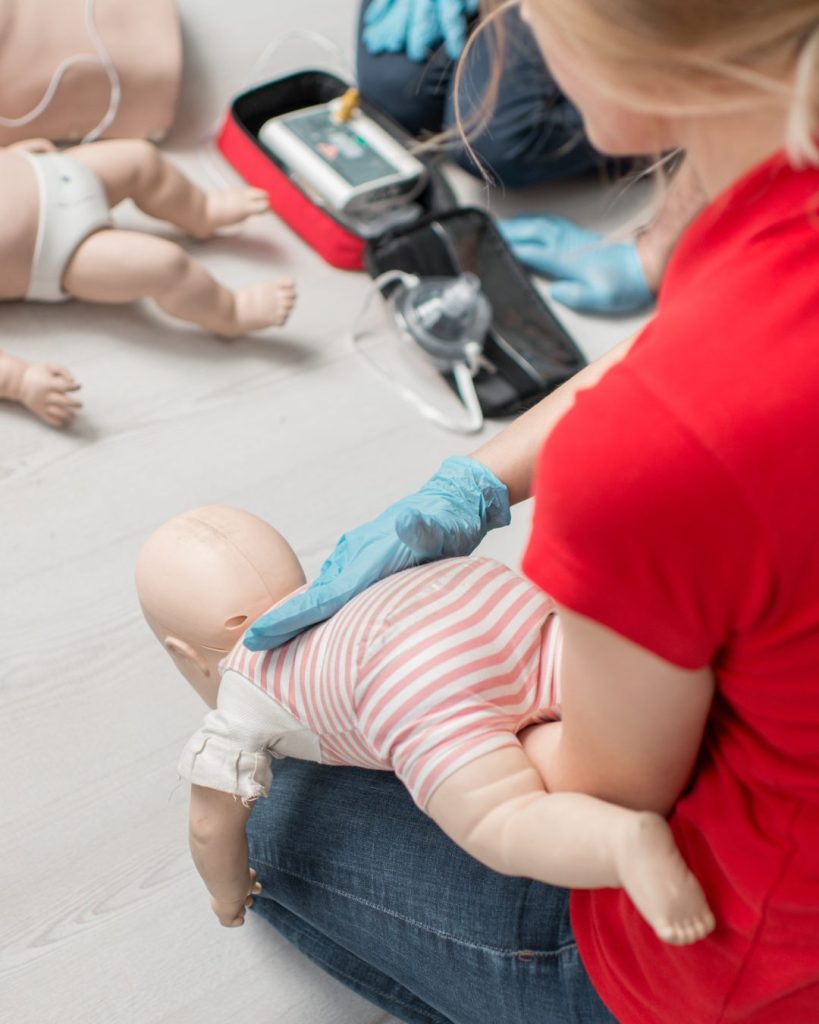

Step 1: Position the Baby
- Sit down and lay the baby face down on your thigh or forearm, ensuring their head is lower than their body.
Step 2: Administer Back Blows
- Give up to 5 sharp back blows between the shoulder blades with the heel of your hand.
Step 3: Perform Chest Thrusts
- If back blows do not relieve choking, lay the baby face up along your legs.
- Use two fingers to administer up to 5 chest thrusts just below the nipple line.
Step 4: Call for Help
- If the object remains lodged, call 999 immediately, continuing back blows and chest thrusts until help arrives.
The Importance of Staying Calm
Witnessing someone choke can be frightening, and you may not feel calm in that moment. It’s essential to remain calm or at least pretend to be calm. Your demeanour can influence how the choking person feels and can make your actions more effective. If you need to call emergency services, do so confidently and follow their instructions.
What to Expect When You Call 999
When you call 999, the operator will ask you a series of questions to assess the situation and dispatch help. Here’s what you can expect:
- Location: Be prepared to provide the exact location of the emergency.
- Nature of the Emergency: Explain that someone is choking and describe the symptoms you observe.
- Condition of the Person: Inform them if the person is conscious or unconscious.
- First Aid Actions Taken: Let them know what first aid you have already administered, such as back blows or abdominal thrusts.
The operator may provide you with further instructions on how to assist the person until help arrives. It’s important to stay on the line and follow their guidance carefully.
Conclusion
Knowing how to respond to choking can save lives. Whether it’s an adult, child, or baby, understanding the appropriate first aid steps can make a significant difference in an emergency. Always remember to seek help from medical professionals after any choking incident, even if the object appears to be dislodged, as injuries may still occur.
For further information, refer to reputable sources like the NHS, British Red Cross, and the American Academy of Pediatrics. Staying informed and prepared is your best defence against choking emergencies.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this blog regarding choking is intended for educational purposes only. It is crucial to seek training from a reputable source, such as St John’s Ambulance, to ensure you are equipped with the most accurate and effective techniques. Please note that guidelines and recommendations regarding choking management may change over time, so it is important to stay informed and up to date.
I do not accept any liability for the information presented on this blog, and it should not be considered a substitute for professional training or medical advice. Always consult a qualified professional for specific guidance and assistance.


